Repeated abortion or habitual abortion
It is also known as recurrent pregnancy loss.
Regarding epidemiology, it should be noted that the incidence of clinical abortion in the general population is 12-15%. The incidence of recurrent miscarriage is not entirely determined accurately by conceptual differences (two or three previous miscarriages), but it is accepted that it affects 1-5% of women.
It is important to know the risk of recurrent miscarriage when counseling couples with pregnancy loss.
*Couples with a single miscarriage do not require specific assessment, however, if your specialist doctor provides adequate and detailed information, as well as emotional support for future pregnancies and your immediate well-being, this will help substantially.
Among the causes associated with recurrent pregnancy loss are the following factors:
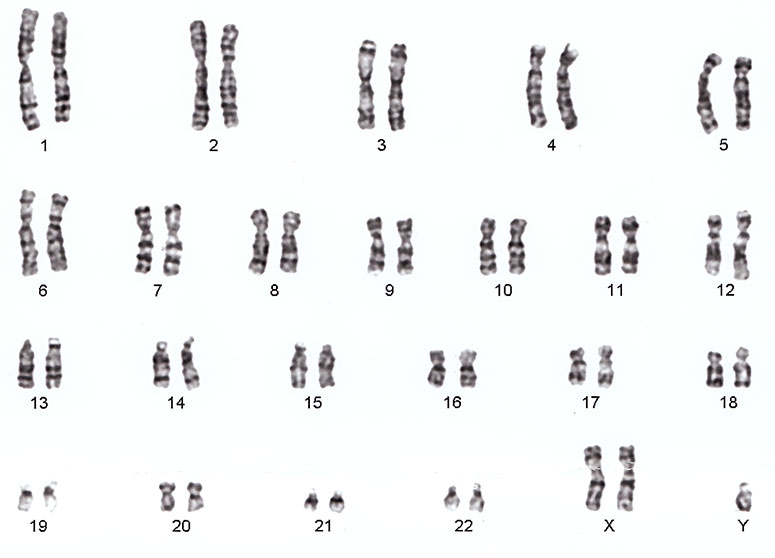
The five most frequent factors were listed first. It is very valuable when making a diagnosis of recurrent miscarriage to make patients understand that there are initial basic studies and other more sophisticated ones that lead us to rule out these factors and/or assess their significance in this problem.
Most importantly, studies for repeat miscarriage are disaggregated and done systematically.
We can enumerate the studies for diagnosis below, concisely mentioning each one of them.
General considerations.
Do not forget that close to 50% of the patients that we study with recurrent abortion will have the aforementioned studies normal. So we must have some principles to consider:
Actuando de acuerdo en estos principios terapéuticos generales y los expuestos por cada causa potencialmente tratable, las expectativas de conseguir un hijo vivo en la mujer con aborto de repetición supera el 75%.
Nuestra recomendación finalmente es: